लोक सेवा आयोग
नेपाल आयल निगम लिमिटेड, प्राविधिक, विविध, पाँचै, वरिष्ठ सहायक (कम्प्युटर) पदको
प्रतियोगितात्मक लिखित परीक्षा
२०७७/१०/२३
KEY [D]
समयः २ घण्टा ३० मिनेट
Multiple Choice
विषयः कम्प्युटर सम्बन्धी
Section 'A': Objective
पूर्णाङ्क : १००
50x1=50 Marks
-
DIR command in DOS is used to
A) display a list of files in a directory
B) display contents of files in directory
C) display type of files in a sub directory
D) all of the above -
Maximum length of DOS command using any optional parameter is
A) 26 characters
B) 87 characters
C) 127 characters
D) 130 characters -
Which one is not a system tool?
A) Backup
B) Disk defragment
C) Virus scanning
D) All of the above -
Which of the following is an essential file of a MS-DOS boot disk?
A) COMMAND.COM
B) START.COM
C) TREE.COM
D) VER.COM -
To modify AutoCorrect options, click options button from File menu, and then click
A) Replace
B) Format
C) Edit
D) Proofing -
The paragraph indentation settings are left, right, and
A) full
B) center
C) special
D) block -
Shortcut for open dialog box in MS Word is
A) Alt + F12
B) Ctrl + F12
C) Shift + F12
D) F12 -
Which of the following shortcut key is used to check spelling in MS Word document?
A) F1
B) F4
C) F6
D) F7 -
It is possible to ______ a data source before performing a merge.
A) create
B) modify
C) sort
D) all of the above -
Landscape is
A) a font style
B) page orientation
C) paper size
D) page layout -
Which of the following typically appear at the end of document for citation of source?
A) End notes
B) Foot notes
C) Header
D) Footer -
Insert Date, Format Page Number and Insert Auto Text are buttons on the ______ toolbar.
A) Formatting
B) Header and Footer
C) Standard
D) Edit -
A feature in MS Words that enables users to send a similar letter or document to multiple recipients is called
A) email
B) express mail
C) document merge
D) mail merge -
What is the purpose of inserting header and footer in document?
A) to enhance the overall appearance of the document
B) to mark the starting and ending of page
C) to make large document more readable
D) to allow page headers and footers appear on document when printed -
In MS-Excel which function enters today's date in a cell?
A) TODAY()
B) DATE()
C) NOW()
D) WEEKDAY() -
Which of the following keys are used to create a chart of the data in the current range in MS-Excel?
A) Alt + F2
B) Alt + F1
C) Shift + Alt + F4
D) Alt + F5 -
You can use the horizontal and vertical scroll bars in excel to
A) split a worksheet into two panes
B) view different rows and columns
C) edit the contents of a cell
D) view different worksheets -
The intersection of a column and a row on a worksheet is called
A) Column
B) Value
C) Address
D) Cell -
Which of the following contains the name of each record on the chart?
A) cell
B) title
C) axis
D) legend -
Formatting a cell in Number format you can't set
A) Decimal places
B) Use 1000 separator
C) Negative numbers
D) Currency symbol -
What does COUNTA() function do in excel?
A) counts a cells having alphabets
B) counts selected cells
C) counts empty cells
D) counts non-empty cells -
B7:B9 indicates
A) Cells B7 and cell B9 only
B) Cells B7 through B9
C) Cell B8 only
D) None of the above -
The term "data series" in the chart wizard refers to
A) a chart legend
B) a group of related data points or markers
C) a set of values plotted in a chart
D) a data label -
____ is a feature in MS Excel that allows to collaborate on a workbook with multiple people.
A) Collaborate
B) Shareit
C) Shared Workbooks
D) Sharepoint -
Which of the following is not a logical database structure?
A) Chain
B) Network
C) Tree
D) Relational -
Which of the following is not a database object?
A) Tables
B) Queries
C) Relationships
D) Reports -
The tool to print information from database table is
A) macro
B) query
C) report
D) form -
Cascade Delete option in MS Access is used to
A) delete all the records of all tables in a database
B) repeat the recent delete operation to all the records of current table
C) ensure that all the related records will be deleted automatically when the record from parent table is deleted
D) delete all the tables in a database -
How can you link a table with another so that a field in current table will display values from a dropdown box from another table while entering data?
A) Query Wizard
B) Look up Wizard
C) Form Wizard
D) Report Wizard -
How to close a presentation in PowerPoint?
A) Ctrl + C
B) Ctrl + O
C) Alt + O
D) Ctrl + W -
Special effects used to introduce slides in a presentation are known as
A) transitions
B) effects
C) animations
D) annotations -
To insert a new slide in the current presentation, we can choose
A) Ctrl + M
B) Ctrl + N
C) Ctrl + O
D) Ctrl + F -
HTML web pages can be read and rendered by....
A) Compiler
B) Server
C) Web Browser
D) Interpreter -
What is the correct syntax in HTML for creating a link on the webpage?
A)
<LINK SRC="PSC.GOV.NP">B)
<BODY LINK="PSC.GOV.NP">C)
<A SRC="PSC.GOV.NP">D)
<A HREF="PSC.GOV.NP"> -
An HTML tag consists of the element name (usually an abbreviation of a longer descriptive name) within which of the following brackets?
A) round brackets
B) square brackets
C) curly brackets
D) angle brackets -
Tracks in hard disk are further divided into
A) Vectors
B) Sectors
C) Clusters
D) Packets -
A half byte is known as....
A) bug
B) nibble
C) data
D) bit -
Which of the following unit is used to describe the printing resolution?
A) Dot per sq. inch
B) Dot per inch
C) Dots printed per unit time
D) All of the above -
____ is the time required by a sector to reach below read/write head.
A) Seek time
B) Latency time
C) Access time
D) None of the above -
Which of the following is NOT a component of a WiFi network?
A) An access point
B) A wireless LAN controller
C) A wireless client
D) A Bluetooth controller -
A computer ...... is a malicious code which self replicates by copying itself to other programs.
A) program
B) virus
C) application
D) worm -
The BIOS found in IBM compatible personal computers is an example of a
A) firmware
B) software
C) output device
D) input device -
Which of the following is not an input unit device?
A) scanner
B) camera
C) plotter
D) digitizer -
The WWW (World Wide Web) is a classic example of
A) computer software
B) operating system
C) hypermedia
D) multimedia -
Which one is the largest space?
A) kilobyte
B) petabyte
C) terabyte
D) gigabyte -
Telnet ......
A) is used to send email
B) uses telephone lines
C) is a protocol that allows for remote login
D) is part of Netscape -
Full form of JPEG is ......
A) Joint Photographic Experts Group
B) Joint Picture Exports Group
C) Joint Picture Export Graphics
D) Joint Picture Extra Group -
ADSL stands for
A) asynchronous digital subscriber line
B) asymmetric digital subscriber link
C) asymmetric digital subscriber line
D) asynchronous digital subscription line -
Firmware is generally written in
A) RAM
B) ROM
C) Hard Disk
D) Cache -
Which of the following is single-user operating systems?
A) MS-DOS
B) UNIX
C) Linux
D) OS/2
Section 'B': Subjective (50 Marks)
A computer system is an electronic device that processes data to perform a wide range of tasks. It consists of both hardware and software components. The computer takes input, processes it, and provides an output. It is capable of performing arithmetic and logical operations, storing data, and executing instructions automatically.
Components of a Computer SystemThe components of a computer system can be divided into two main categories:
- Hardware: The physical parts of the computer.
- Software: The set of instructions (programs) that tells the hardware what to do.
- Input Unit: Used to feed data into the computer (e.g., keyboard, mouse).
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The brain of the computer that performs instructions. It consists of:
- Control Unit (CU): Directs the flow of data.
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU): Performs arithmetic and logical operations.
- Registers: Temporary storage for quick data processing.
- Memory Unit: Stores data temporarily (RAM) or permanently (hard drive).
- Output Unit: Converts processed data into human-readable form (e.g., monitor, printer).
- Storage Unit: Where data is saved (e.g., HDD, SSD).
- Bus System: Transfers data between components (data bus, address bus, control bus).
- Motherboard: The main circuit board that connects all components.
Below is a basic block diagram illustrating how the components interact:
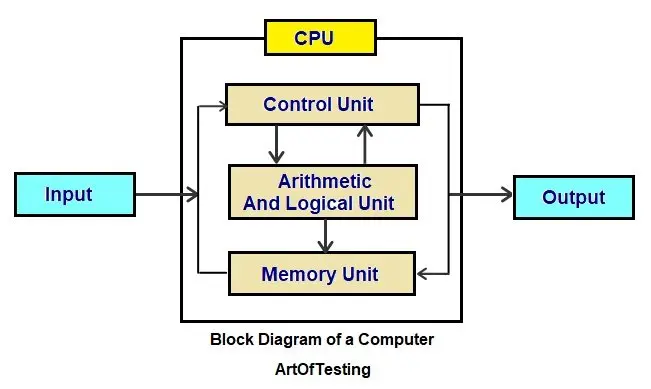
Explanation of the Block Diagram:
- Input Unit: Takes user input and sends it to the CPU.
- CPU: Processes the data and performs calculations.
- Memory Unit: Stores data temporarily or permanently.
- Output Unit: Converts processed data into a readable format.
2) What are the functions of Operating System? What are basic measures that you can take in order to tune and maximum the performance of windows operating system? 2+8=10
An Operating System (OS) is system software that manages the hardware and software resources of a computer, providing an interface between the user and the machine. Its primary functions include:
Functions of an OS:- Process Management: The OS manages the execution of processes, ensuring that each process gets enough CPU time and that multiple processes can run simultaneously without interference (multitasking).
- Memory Management: The OS allocates memory to processes and manages it to ensure efficient usage, preventing memory leaks and making sure no process accesses unauthorized memory areas.
- File System Management: The OS organizes and manages files on storage devices. It handles operations like file creation, deletion, reading, and writing, ensuring data is stored in an organized manner.
- Device Management: The OS manages input and output devices (printers, keyboards, mice, etc.), coordinating communication between hardware and software.
- Security and Access Control: The OS ensures that unauthorized users or processes do not access the system. It manages user accounts, permissions, and security protocols (e.g., authentication and encryption).
- User Interface: The OS provides a graphical or command-line interface for users to interact with the computer and run applications.
- Network Management: The OS manages communication between computers in a network, ensuring data is transmitted securely and efficiently.
- Error Handling: The OS detects, reports, and corrects errors that may occur during process execution, memory access, or device communication.
To ensure your Windows operating system runs smoothly and efficiently, here are some basic measures you can take to tune and optimize its performance:
- Disable Startup Programs: Many applications set themselves to run at startup, which can slow down boot times and overall performance. You can disable unnecessary startup programs via the Task Manager.
Steps: Right-click the Taskbar → Task Manager → Startup tab → Disable unnecessary programs. - Uninstall Unnecessary Software: Over time, unused programs can clutter your system and consume valuable resources. Regularly uninstall unnecessary or rarely used programs to free up space and improve performance.
Steps: Go to Control Panel → Programs and Features → Uninstall unnecessary applications. - Update Windows and Drivers: Keep your Windows OS and device drivers updated to ensure optimal performance and security. Updates often contain bug fixes and performance improvements.
Steps: Go to Settings → Update & Security → Check for Updates. - Run Disk Cleanup: Windows stores temporary files, cache, and other unnecessary files that can take up space and slow down the system. Use Disk Cleanup to remove these.
Steps: Search for Disk Cleanup in the Start menu → Select the drive → Click OK → Clean up system files. - Defragment Hard Drive (HDD): Over time, data on hard disk drives (HDDs) can become fragmented, slowing down access speeds. Use Disk Defragmenter to reorganize fragmented data and improve performance.
Steps: Search for Defragment and Optimize Drives in the Start menu → Select the drive → Click Optimize. - Adjust Visual Effects: Windows provides various visual effects that can consume significant system resources. You can disable or adjust these effects for better performance.
Steps: Right-click This PC → Properties → Advanced system settings → Settings under Performance → Select Adjust for best performance or customize specific options. - Increase Virtual Memory (Paging File): Virtual memory acts as an extension of your physical RAM. Increasing the size of the paging file can improve performance, especially if you're running memory-intensive applications.
Steps: Go to Control Panel → System and Security → System → Advanced system settings → Performance → Settings → Advanced → Virtual Memory → Increase paging size. - Disable Background Services: Some background services may not be essential for your daily tasks. Disabling non-essential services can free up system resources.
Steps: Press Windows + R, type services.msc, and disable unnecessary services. - Check for Malware and Viruses: Malware or viruses can slow down your computer. Regularly scan your system using built-in tools like Windows Defender or third-party antivirus software.
Steps: Go to Settings → Update & Security → Windows Security → Virus & threat protection → Run a quick or full scan. - Upgrade Hardware (RAM/SSD): If your system is old, consider upgrading the hardware, such as adding more RAM or switching from a hard disk drive (HDD) to a solid-state drive (SSD). SSDs significantly improve boot times and application load speeds.
A section break in MS Word is a formatting tool that divides a document into sections, allowing users to apply different formatting (such as margins, headers/footers, columns, page orientation, and more) to each section. By using section breaks, you can create parts of a document that have unique formatting, without affecting the rest of the document.
Types of Section Breaks in MS Word:- Next Page: This section break starts a new section on the next page. It is useful when you want to apply different formatting or page numbering from the next page onward (e.g., when starting a new chapter in a book or report).
- Continuous: A continuous section break starts a new section on the same page. This is useful when you want to change the number of columns or layout format within a page without starting a new page.
- Even Page: This type of section break starts a new section on the next even-numbered page. It is typically used for documents that will be printed double-sided, where chapters or sections always begin on the left-hand side of the document.
- Odd Page: This section break starts a new section on the next odd-numbered page. It is often used in double-sided documents where new sections should always start on the right-hand side of the document.
A chart in Excel is a graphical representation of data. It allows users to visualize numerical data in the form of graphs, making it easier to analyze trends, patterns, and relationships within the dataset. Charts are often used to summarize and present data in a more understandable and meaningful way.
Types of Charts in Excel:- Column Chart: A column chart displays data in vertical bars, where each bar represents a category. This type of chart is useful for comparing different categories or tracking changes over time. It is commonly used for showing values across a few categories.
- Line Chart: A line chart connects individual data points with a line, showing trends or changes over time. It is ideal for displaying data trends or comparisons over a period, such as stock prices or sales over months.
- Pie Chart: A pie chart represents data as slices of a circle. Each slice represents a category, and its size is proportional to the value of that category. It is best for showing proportions or percentages of a whole.
- Bar Chart: Similar to a column chart, but with horizontal bars. It is used when comparing multiple categories of data and is helpful when you have long category names that fit better along the Y-axis.
- Scatter Chart (XY Chart): A scatter chart displays data points on a two-dimensional grid. It shows the relationship between two variables by plotting points at their intersections. This type of chart is useful for identifying correlations or patterns between two datasets.
In MS Access, data types define the kind of data that can be stored in each field of a table. The appropriate data type ensures efficient data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
Six Common Data Types in MS Access and Their Storage Sizes:-
Text (Short Text):
- Description: Stores text or combinations of text and numbers.
- Storage Size: Can hold up to 255 characters.
- Usage: Suitable for storing names, addresses, or other text-based data where a large amount of text is not required.
-
Memo (Long Text):
- Description: Used for large text entries, such as descriptions or notes.
- Storage Size: Can store up to 65,536 characters.
- Usage: Suitable for comments, long descriptions, or notes that exceed the 255-character limit of the Short Text data type.
-
Number:
- Description: Stores numerical values, either integer or floating-point numbers.
- Storage Size:
- Byte: 1 byte (0 to 255)
- Integer: 2 bytes (-32,768 to 32,767)
- Long Integer: 4 bytes (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647)
- Single: 4 bytes (floating-point numbers)
- Double: 8 bytes (floating-point numbers)
- Usage: Used for mathematical calculations or storing numeric values like age, price, or quantity.
-
Date/Time:
- Description: Stores date and time values.
- Storage Size: 8 bytes.
- Usage: Used for recording dates and times, such as birth dates, appointment times, or invoice dates.
-
Currency:
- Description: Stores currency values and avoids rounding errors during calculations.
- Storage Size: 8 bytes.
- Usage: Ideal for storing financial data, such as prices, costs, or salaries.
-
AutoNumber:
- Description: Automatically generates a unique number for each new record.
- Storage Size: 4 bytes (Long Integer).
- Usage: Often used for primary key fields where a unique identifier is required, such as order IDs or customer numbers.
MS PowerPoint is a powerful presentation software used for creating professional slideshows. Its importance lies in the following:
- Visual Communication: PowerPoint enables the use of text, images, charts, videos, and other multimedia elements to communicate information clearly and effectively.
- Professional Presentations: Widely used in business, education, and conferences, PowerPoint allows users to create visually appealing presentations for meetings, lectures, and pitches.
- Ease of Use: With an intuitive interface, pre-designed templates, and customizable slide layouts, users can quickly create presentations without requiring advanced design skills.
- Interactive Features: PowerPoint offers features like hyperlinks, buttons, and animations to make presentations more interactive and engaging.
- Collaboration: Teams can work together on presentations, with easy sharing and collaborative editing features.
| Aspect | Slide Transition | Custom Animation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visual effects applied when moving from one slide to the next during a presentation. | Visual effects applied to individual elements (text, images, shapes) within a slide. |
| Usage | Affects the entire slide during the transition from one slide to another. | Affects specific objects within a slide, animating their appearance, movement, or behavior. |
| Types of Effects | Fade, Slide, Wipe, Dissolve, etc. | Entrance, Exit, Emphasis, and Motion Path effects. |
| Timing | Occurs between slides. | Occurs during the display of a slide. |
| Purpose | Enhances the flow between slides to maintain audience attention. | Draws attention to important elements, controls the order of appearance, and emphasizes key points. |
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used for creating and designing web pages and web applications. It consists of a series of elements (tags) that define the structure of a webpage, such as headings, paragraphs, links, images, and more. These elements are written in text files and interpreted by web browsers to display content on the internet.
Importance of HTML in the World Wide Web- Foundation of Web Development: HTML forms the backbone of almost every website. It structures content on the web, allowing text, images, links, and multimedia to be displayed by web browsers.
- Interactivity and Hyperlinks: HTML allows linking to other pages through hyperlinks, which forms the essence of web navigation, creating the interconnected network known as the World Wide Web.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: HTML works across all devices and operating systems, allowing web content to be accessed anywhere, on any device, making the web universally accessible.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Proper use of HTML tags helps in optimizing websites for search engines, improving website visibility, and enhancing user experience.
- Integration with Other Technologies: HTML integrates seamlessly with other web technologies like CSS (for styling) and JavaScript (for interactivity), making it essential for modern web development.


